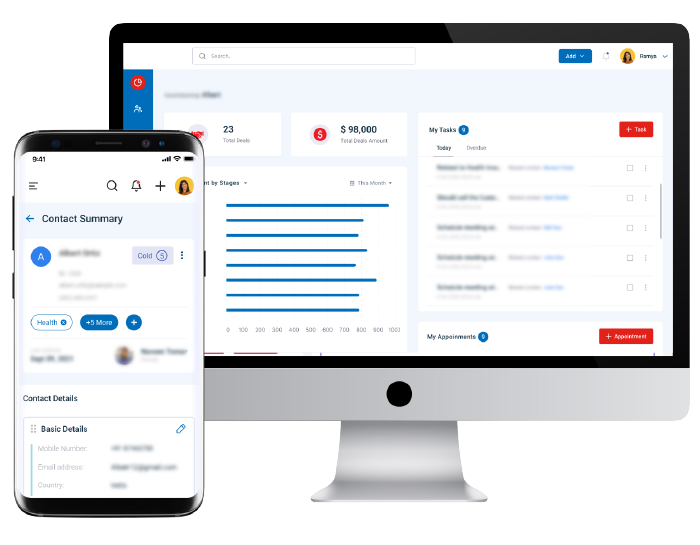
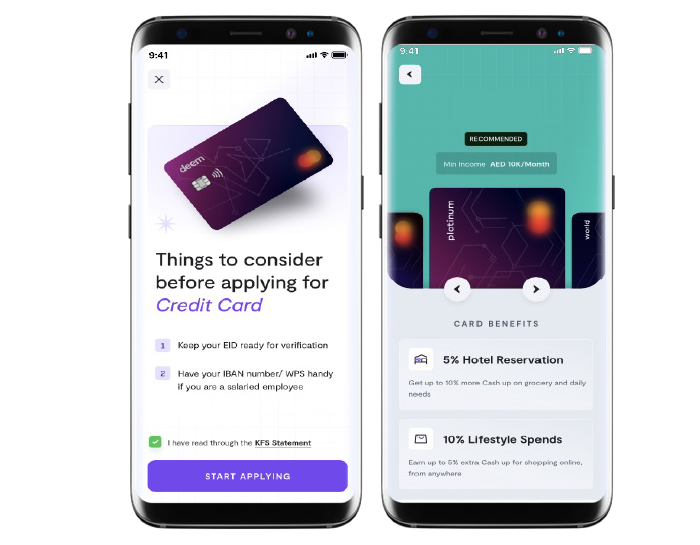
These global innovators grew with us
You can too.
With a partner that helps you

Turn your Digital Dreams
into Reality
with unique design thinking and technology building blocks.
Dream Big and Transform
Business Incrementally
with de-risked and trusted approaches.
Revitalize ROI and Boost
Customer Retention
with Neutrinos Infinity Composer.
Achieve Limitless Potential
with a Global Ecosystem
of top-tier vendors and transformation programs.
Just like these inspiring stories did
At Neutrinos, we empower your success by bringing your digital aspirations to life and championing a culture of prosperity that delivers business value across categories.
Enter the Neutriverse of imagination
And grow further with our partners
We don’t just keep great company. We also help others at it!
It’s not just our customers, but our partners too!
Our ecosystem is home to many stories of businesses reimagining their digital footprint with our fast and efficient deployment capabilities.
Discover what’s NEU at Neutrinos